News
-
Biomaterial developed at São Paulo State University proves capable of accelerating bone regeneration
2023-11-21In vitro experiments showed cobalt-doped calcium phosphate to be capable of stimulating bone cell differentiation by mimicking a low-oxygen environment. Next steps include animal testing. -
Identified a star capable of forming a magnetar, the most powerful type of magnet in the Universe
2023-11-15A little smaller than the Sun but ten times as hot, it will go supernova and become a neutron star with a magnetic field 100 trillion times stronger than Earth’s. -
In Northeast Brazil, rabies virus variants from marmosets are found in bats
2023-11-15The emergence of rabies in distinct wildlife species is a potential source of human infection and poses life-threatening risks. As the researchers responsible for the discovery warn, anyone who comes into contact with these animals should alert the authorities. A 36-year-old farm worker died in May, only weeks after being bitten by a marmoset. -
The crucial role of biofuels in the energy transition is explained in an encyclopedic new book
2023-11-15Written by two experts on biofuels, Luís Augusto Barbosa Cortez and Frank Rosillo-Calle, the book explores Brazil’s experience and how other countries can learn from it in the context of climate change. -
Platform identifies soil microorganisms that cause disease
2023-11-15Technology developed by the startup ByMyCell with the support of FAPESP helps farmers make decisions that boost yields and reduce the use of agrochemicals. -
Global funders of health-related research discuss epidemic and pandemic preparedness guidelines
2023-11-15The Ninth General Assembly of the Global Research Collaboration for Infectious Disease Preparedness, representing funding agencies, research institutions and government bodies from around the world, was held at FAPESP in São Paulo, Brazil, on October 24-25. -
Novel method facilitates study of oxidized lipids involved in neurodegenerative diseases
2023-11-14Scientists at the University of São Paulo’s Center for Research on Redox Processes in Biomedicine used a novel technique they themselves developed to identify altered molecules in an animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). -
Molecule tested at University of São Paulo proves able to mitigate heart failure
2023-11-08Results of trials involving animals, cell cultures and human heart tissue are reported in the European Heart Journal. The study was conducted by researchers at USP in partnership with a biopharmaceutical firm, offering hope to 2 million Brazilians who suffer from the disease. -
El Niño, climate change and deforestation: scientists explain what may lie behind the drought in the Amazon
2023-11-08Brazil’s North region is experiencing the worst drought of the century, with severe social and economic impacts. The problem was discussed at an event hosted by FAPESP on October 17. -
New center will use data and artificial intelligence to support public safety policymaking
2023-11-08FGV Analytics is a partnership involving FAPESP, Getúlio Vargas Foundation, the University of São Paulo and the São Paulo State Department of Public Safety. Its mission includes fostering development of evaluation tools and evidence-based public policy. -
Customizable corporate training system uses technology, immersion and interactivity
2023-11-08The platform was developed by a startup supported by FAPESP. It uses an adult learning methodology that leverages motivational techniques and customization. -
South African researcher presents novel ways of thinking about the relations between society and ecosystems
2023-11-08Laura Maureen Pereira delivered the Seventh 2023 FAPESP Lecture on “Why we need transformative scenarios for people and nature”. -
Open data sharing is essential to pursuit of sustainability solutions
2023-11-08This was a consensus among representatives of funding agencies in the Americas who met virtually in October under the aegis of the Global Research Council. A previous event discussed funding for research relating to artificial intelligence in Latin America. -
Study reveals bacterial protein capable of keeping human cells healthy
2023-11-08An article published in PNAS by Brazilian and Australian researchers describes a hitherto unknown protein with anti-oxidizing properties secreted by Coxiella burnetii, a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium, pointing to possible treatments for auto-immune diseases and even cancer. -
“We are not so much trying to improve our understanding of human evolution as trying to reduce our ignorance about it”
2023-11-01This is how Bernard Wood, one of the foremost paleoanthropologists alive, summed up his philosophy in the Sixth 2023 FAPESP Lecture. -
Research funding disbursed by FAPESP rose 16.7% in 2022 compared with the previous year
2023-11-01FAPESP increased research funding opportunities by creating new programs and new partnerships, according to its 2002 Annual Report. -
Novel portable device weighing less than 1 kg helps harbor pilots maneuver large vessels into port
2023-11-01High-precision maneuvering support system with integrated hardware and software developed by a startup supported by FAPESP transmits dynamic information in real-time via a smart platform. -
Test detects co-infection by novel species of parasite in severe cases of visceral leishmaniasis
2023-11-01The test developed by Brazilian researchers accurately identifies the causative agent in less than two hours, so that treatment can be properly targeted. Brazil is seeing a growing number of cases of co-infection by protozoans Leishmania infantum and Crithidia. -
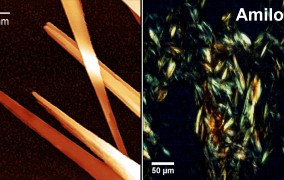
Chemical process makes peptide acquire structure similar to amyloid plaques found in neurodegenerative diseases
2023-11-01Highlighted on the cover of the journal Biochemistry, a study by Brazilian researchers shows that a chemical change called pyroglutamination can occur spontaneously during peptide synthesis. The discovery has implications for laboratory experiments and research on Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and other diseases associated with the formation of amyloid aggregates. -
Better access to diagnostic tests raises incidence of thyroid cancer in more affluent areas
2023-11-01A study compared geographical and socioeconomic dimensions of the disease in São Paulo and the Barretos region. Incidence was far higher in the former but mortality rates were similar, suggesting overdiagnosis in specific areas and social groups. -
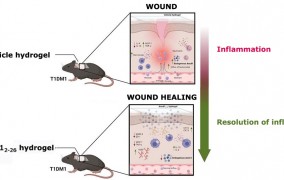
Hydrogel developed by Brazilian researchers improves skin wound healing in diabetics
2023-10-25The product, which contains the anti-inflammatory protein annexin A1, accelerated complete skin wound healing in mice, and has the potential to become part of the arsenal of treatments for a disease that affects 17.7 million Brazilians. -
Longevity may be associated with olfactory perception of harmful substances
2023-10-25In nematode worms exposed to a compound secreted by pathogenic bacteria, researchers observed activation of a neural circuit resulting in a longer lifespan and less protein aggregation, one of the causes of neurodegenerative diseases. The discovery paves the way for the development of treatments for age-related diseases. -
Products made of plastic falsely claimed to be biodegradable are on sale at Brazilian supermarkets
2023-10-25Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo analyzed allegedly biodegradable plastic items sold by 40 supermarkets and found most to be oxo-degradables, banned in several countries because they contribute significantly to microplastic pollution. Bills currently before Brazil’s Congress would regulate the sale of such products. -
Method involving citizen participation is effective to address risks of environmental disaster
2023-10-25A research project showed that mobilizing citizens in flood-prone areas improves data collection and increases resilience. -
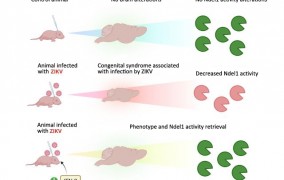
Study associates reduced activity of a key enzyme with microcephaly in zika-infected offspring
2023-10-25Brazilian researchers showed that brain activity of Ndel1, an enzyme that plays an important role in neuron differentiation and migration, decreased in mice infected by zika during pregnancy. The enzyme could become a biomarker for early diagnosis of the congenital syndrome associated with zika. -
Subsistence poaching has little impact on biodiversity in the Amazon’s environmental protection areas
2023-10-25A study conducted in sustainable-use reserves shows that local game species become less abundant about 5 kilometers away from the nearest human community, but the negative effects of anthropic activity can be mitigated by appropriate management strategies. -
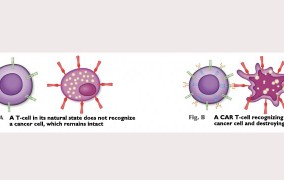
Nutera Advanced Therapy Center will produce CAR T-cells for use in clinical trial of cancer treatment
2023-10-18Opened in 2022 with FAPESP’s support, Nutera is Latin America’s first cellular product manufacturing plant. It is run by researchers from Butantan Institute and the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Blood Center, and could become a supplier to the SUS, Brazil’s public healthcare network. -
In 2020, 30% of the Pantanal was burned to cinders by wildfires
2023-10-18This is one of the findings of a study led by Brazilian scientists and reported in the science journal Fire. The researchers built a model based on images from the SENTINEL-2 satellite and were able to detect burned areas much more accurately. -
Study demonstrates antimicrobial action of polyalthic acid from copaiba oil
2023-10-18Findings reported in the journal Antibiotics by scientists working in Brazil and the United States pave the way for the development of drugs against resistant bacteria. -
Plants in the Cerrado combine at least two strategies to survive fire, study shows
2023-10-18Plant species native to the Brazilian savanna-like biome grow thick bark to protect their internal tissues and hide organs that assure resprouting below the ground, according to an article in Flora by researchers at São Paulo State University. -
Study reveals areas of Brazilian Amazon where no ecological research has been done
2023-10-16The findings evidenced high susceptibility to climate change by 2050 in 15%-18% of the areas with the most neglected biodiversity. -
FAPESP issues two new calls focusing on acceleration and internationalization of deep tech startups
2023-10-16The calls offer opportunities for accelerators and agencies that provide services for startups under the aegis of Tecnova III, a program run by the Brazilian Innovation Agency which in São Paulo is operationalized in partnership with FAPESP. -
Cerrado requires strict protection and rehabilitation of areas to curb deforestation, scientists warn
2023-10-11Record levels of destruction of native vegetation in the Brazilian savanna, the second-largest biome in South America, motivated the letter published in Nature Sustainability. The scientists who wrote it stress the need for specific measures to conserve the Cerrado’s rich biodiversity. -
Researcher who transformed soil physics and vadose zone hydrology delivers fifth 2023 FAPESP Lecture
2023-10-11Dutch-born scientist Martinus Theodorus van Genuchten is the author of a famous equation describing the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soil. His discoveries are central to agricultural operations and climate science, and he recently won the prestigious Wolf Prize in Agriculture. -
FAPESP seeks to attract investment in small enterprises that participate in its pro-innovation program
2023-10-11Two calls have been issued to register equity crowdfunding platforms and angel investor networks interested in investing in deep techs. -
Novel biomaterial delivers medication directly to fish gut
2023-10-11In addition to helping combat antimicrobial resistance, the bioparticle developed at the Federal University of São Paulo avoids the waste and pollution created by excessive amounts of drugs in water bodies. The strategy was tested on an ornamental fish species native to the Amazon and found to be safe. -
Absorption of light by molecules has applications in microscopy, medicine and data storage
2023-10-11An alternative method proposed by a Brazilian physicist cuts the time for computer simulation of the absorption spectrum from two days to a few hours. -
Perfect storm: poor sleep quality worsens health problems in obese older people, study shows
2023-10-10Research conducted at the University of São Paulo involving 95 volunteers associated poor sleep quality with a deterioration in the complications caused by aging and overweight, such as anxiety, depression, body fat gain, and loss of muscle mass and strength. -
Amazon+10 Initiative and CNPq issue new call to support scientific expeditions in the region
2023-10-04Subnational funding agencies and Brazil’s National Scientific Council will partner to allocate almost BRL 60 million to research projects that explore little-known areas of the world’s largest tropical forest. -
Researcher assessment criteria are changing globally
2023-10-04According to experts interviewed by Agência FAPESP, classic indicators based on numbers of articles and citations are being replaced by a multidimensional approach that encompasses teaching, research, extension, culture and outreach. -
FAPESP assembles experts to discuss the Amazon during UN Science Summit in New York
2023-10-04‘Amazon Day: Science for the Amazon’ was held on September 15, during the 78th United Nations General Assembly. Panelists discussed the role of science, technology and innovation in sustainable development for the region. -
Study identifies six drugs that can be repurposed for treatment of toxoplasmosis
2023-10-04Brazilian researchers screened 160 compounds known to be effective against SARS-CoV-2 and identified those that also act against the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. The most promising will be tested in humans for treatment of the chronic form of the disease. -
Discovery of mechanism involved in dental inflammation paves way to therapies against bone loss
2023-10-04Researchers at the University of São Paulo showed in mice the importance of the signaling pathway mediated by the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and its receptor TNFR1; the discovery could now help scientists develop medications for oral health. -
Biofungicide based on essential oils developed to combat soybean disease
2023-10-04The technology was invented by a FAPESP-supported startup. It consists of a blend of essential oils from various plants, encapsulated in natural polymers that release the biofungicide gradually over a long period. -
Study shows how ‘superbacteria’ were prevented from spreading in a large tertiary hospital
2023-10-02The study was conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo, highlighting the importance of identify and isolating infected patients on admission to the emergency room. The findings also showed that containment may be impaired if patients stay more than two days in the ER. -
FAPESP issues call for investment funds to boost support for innovation
2023-09-27The call is one of several initiatives designed by FAPESP to help science and technology startups supported by its entrepreneurship and innovation program attract investors and survive “death valley”. -
Risk of eating disorders among vegan diet followers is low, study suggests
2023-09-27The prevalence of dysfunctional eating behaviors among almost 1,000 vegans studied by researchers at the University of São Paulo was less than a tenth of the average for the Brazilian population. The explanation, according to the researchers, lies in the reasons for which people choose a restrictive diet. -
Specialists discuss priorities for energy transition in aviation
2023-09-27A seminar hosted by the steering committee for the FAPESP Bioenergy Research Program featured researchers and representatives of the public and private sectors. A rapid and substantial increase in production of sustainable aviation fuels was the option considered most consistent. -
Study could lead to treatment for a type of cancer that affects children’s endocrine system
2023-09-27Experiments conducted at the University of São Paulo showed that expression of the gene that encodes the vitamin D receptor is greatly reduced in pediatric adrenocortical tumor cells. When the gene was activated, an anti-proliferation effect was observed. The only treatment currently available is surgical removal of the tumor. -
Researchers create formula for first synthetic sugarcane molasses with fully reproducible composition
2023-09-27The product will pave the way for researchers and food engineers to develop novel industrial processes based on the use of sugarcane molasses. It was tested as a yeast culture medium for ethanol production.
Most popular
-
Study identifies molecular alterations in brain tissue and blood of people who committed suicide
2024-03-13
-
Study helps explain why stress in adolescence can lead to predisposition to mental illness in adulthood
2024-01-24
-
Study shows that Rio Grande Rise was once a giant mineral-rich tropical island near Brazil
2024-01-31
-
Butantan Institute’s dengue vaccine protects 79.6% of those vaccinated, study shows
2024-02-01
-
Brazilian researcher helps describe a novel species of jellyfish discovered in a remote location in Japan
2024-01-31
-
Growth hormone influences regulation of anxiety via a specific group of neurons
2024-01-02
-
Amphibians use scream inaudible to humans for self-defense against predators, study suggests
2024-04-03
-
Biodegradable sensor monitors levels of pesticides via direct contact with surface of fruit and vegetables
2024-01-31
-
Weight training improves symptoms of anxiety and depression in old people, study confirms
2024-04-10
-
Study reveals evidence of violence at a time of crisis in ancient Peru
2024-03-27