

Left, Aspergillus fumigatus exposed for 48 hours to traditional antifungals caspofungin (top) and voriconazole (bottom). Right, combination of these drugs with brilacidin eliminated most of the fungus (photo: researchers’ archive)
Combinations of antifungals with brilacidin, a drug undergoing clinical trials for other diseases, cleared up lung infections in animals. On its own, the candidate drug treated a fungal disease of the cornea that affects millions of people worldwide.
Combinations of antifungals with brilacidin, a drug undergoing clinical trials for other diseases, cleared up lung infections in animals. On its own, the candidate drug treated a fungal disease of the cornea that affects millions of people worldwide.
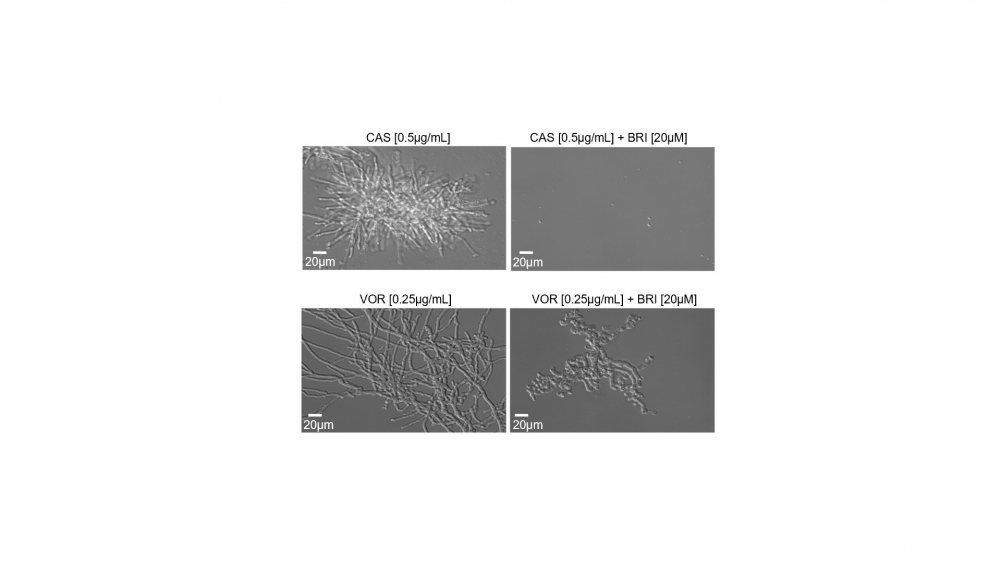
Left, Aspergillus fumigatus exposed for 48 hours to traditional antifungals caspofungin (top) and voriconazole (bottom). Right, combination of these drugs with brilacidin eliminated most of the fungus (photo: researchers’ archive)
By André Julião | Agência FAPESP – A study conducted at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil shows that brilacidin, a new drug tested for treatment of diseases ranging from bacterial skin infections to COVID-19, can kill drug-resistant strains of fungi when combined with two classes of antifungals available on the market.
This potential application of the drug has been patented and is reported in an article published in Nature Communications. It was discovered by researchers at the Ribeirão Preto School of Pharmaceutical Sciences (FCFRP-USP) supported by FAPESP.
The problem of drug resistance is a challenge recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO), but developing new drugs is costly and time-consuming. “For this reason, we set out to identify the antifungal activity of known chemical molecules that had not been studied for their effects on fungal growth control. In this case, we explored 1,400 chemical compounds until we arrived at brilacidin,” said Thaila Fernanda dos Reis, first author of the article and a postdoctoral fellow at FCFRP-USP.
Thanks to the use of several different methods, the researchers concluded that combining brilacidin with either of two antifungals (caspofungin or voriconazole) could kill resistant strains of several fungal species that cause infections in humans, such as Aspergillus fumigatus, which causes invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.
Aspergillosis is a common infection in intensive care units (ICUs), with mortality rates of between 60% and 90%. It also affects patients with impaired immune systems, such as those undergoing treatment for cancer (read more at: agencia.fapesp.br/39521 and agencia.fapesp.br/36064).
In addition to the combinations with antifungals for lung infections, brilacidin alone blocked growth of A. fumigatus and development of the disease in an animal model of fungal keratitis, an infection of the cornea that affects 1 million-2 million people per year worldwide, especially in tropical countries with intense agricultural activity, as it frequently results from corneal abrasion by plant debris. In the United States and other developed countries, wearing contact lenses contaminated by fungi is the main risk factor.
Action mechanism
Drug resistance comes about when a microorganism (fungus, bacterium or virus) finds a way to survive and continue multiplying even in the presence of a drug that should inhibit its growth. Hence the importance of having several drugs with different action mechanisms so as to be able to choose one drug instead of another if a strain proves resistant.
However, while there are nine classes of anti-bacterials, only four classes of antifungals are commercially available. Caspofungin is an example. It has been available for some time, with an action mechanism that inhibits synthesis of the fungal cell wall, an integrity-related structure surrounding the plasma membrane.
It is not unusual for fungi to activate a repair system on coming into contact with the drug, avoiding the effects of the drug and surviving in its presence. The study pointed to the potential benefits of combining caspofungin with brilacidin in terms of deactivating this repair system.
“Caspofungin doesn’t kill A. furmigatus but hinders its multiplication. This is often sufficient for the host’s immune system to control the infection, but not always, so it’s important to identify drugs that can act in synergy with caspofungin. One option would be to develop a single medication combining caspofungin and brilacidin so that they acted together,” said Gustavo Henrique Goldman, last author of the article and a professor at FCFRP-USP.
Superfungi
Another advantage of brilacidin detected by the researchers was that its combination with caspofungin or voriconazole acted against different species of fungus. In tests involving an animal model, the caspofungin-brilacidin combination was effective against other species besides A. fumigatus, such as Candida albicans, Candida auris and Cryptococcus neoformans.
These and other species are known as superfungi because of their robust resistance to drugs and have been blamed for severe hospital-acquired infections. They recently became more common owing to the many hospitalizations in ICUs during the COVID-19 pandemic (read more at: agencia.fapesp.br/40165 and agencia.fapesp.br/36111).
The researchers found the brilacidin-voriconazole combination to be effective against both A. fumigatus and species in the order Mucorales that cause severe facial deformation and are found mainly in India and Pakistan.
Clinical trials are needed to confirm the effects in humans. In partnership with Innovation Pharmaceuticals Inc. (IPI), the US-based company that owns the patent on brilacidin, the researchers are now looking for a Brazilian company interested in licensing the drug, conducting clinical trials, and marketing one of the combinations, if the trials are successful.
The research also involved another project supported by FAPESP.
The article “A host defense peptide mimetic, brilacidin, potentiates caspofungin antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi” is at: www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37573-y.
Republish
The Agency FAPESP licenses news via Creative Commons (CC-BY-NC-ND) so that they can be republished free of charge and in a simple way by other digital or printed vehicles. Agência FAPESP must be credited as the source of the content being republished and the name of the reporter (if any) must be attributed. Using the HMTL button below allows compliance with these rules, detailed in Digital Republishing Policy FAPESP.





